Holdt
0 Course Enrolled • 0 Course CompletedBiography
The Powerhouse of Industries Diesel Generators for Industrial Applications
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of industrial operations, a reliable and efficient power source is essential to keep businesses running smoothly. Diesel generators have long been the go-to choice for providing backup power in industrial settings due to their robustness, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the world of diesel generators, exploring their design, functionality, applications, and benefits in industrial settings.
History and Evolution of Diesel Generators
The history of diesel generators can be traced back to the late 19th century when Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine. Diesel engines are known for their high efficiency and durability, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, including power generation. The first diesel generator was developed in the early 20th century and since then, diesel generators have become a staple in various industries around the world.
Over the years, diesel generators have undergone significant advancements in terms of design, technology, and efficiency. Modern diesel generators are equipped with sophisticated control systems, advanced fuel injection technology, and enhanced cooling mechanisms to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These advancements have made diesel generators more versatile and adaptable to the diverse needs of industrial applications.
Design and Functionality of Diesel Generators
Diesel generators consist of three main components: the diesel engine, the alternator, and the control system. The diesel engine is responsible for converting chemical energy from diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. This mechanical energy is then used to drive the alternator, which generates electricity through the process of electromagnetic induction. The control system regulates the operation of the diesel generator, monitoring parameters such as voltage, frequency, and load to ensure stable and efficient power output.
Diesel generators are available in a wide range of sizes and configurations to suit different industrial applications. They can be stationary or portable, open or enclosed, and can vary in power output from a few kilowatts to several megawatts. The choice of diesel generator depends on factors such as the power requirements of the industrial operation, the available space, and the environmental conditions in which the generator will be operating.
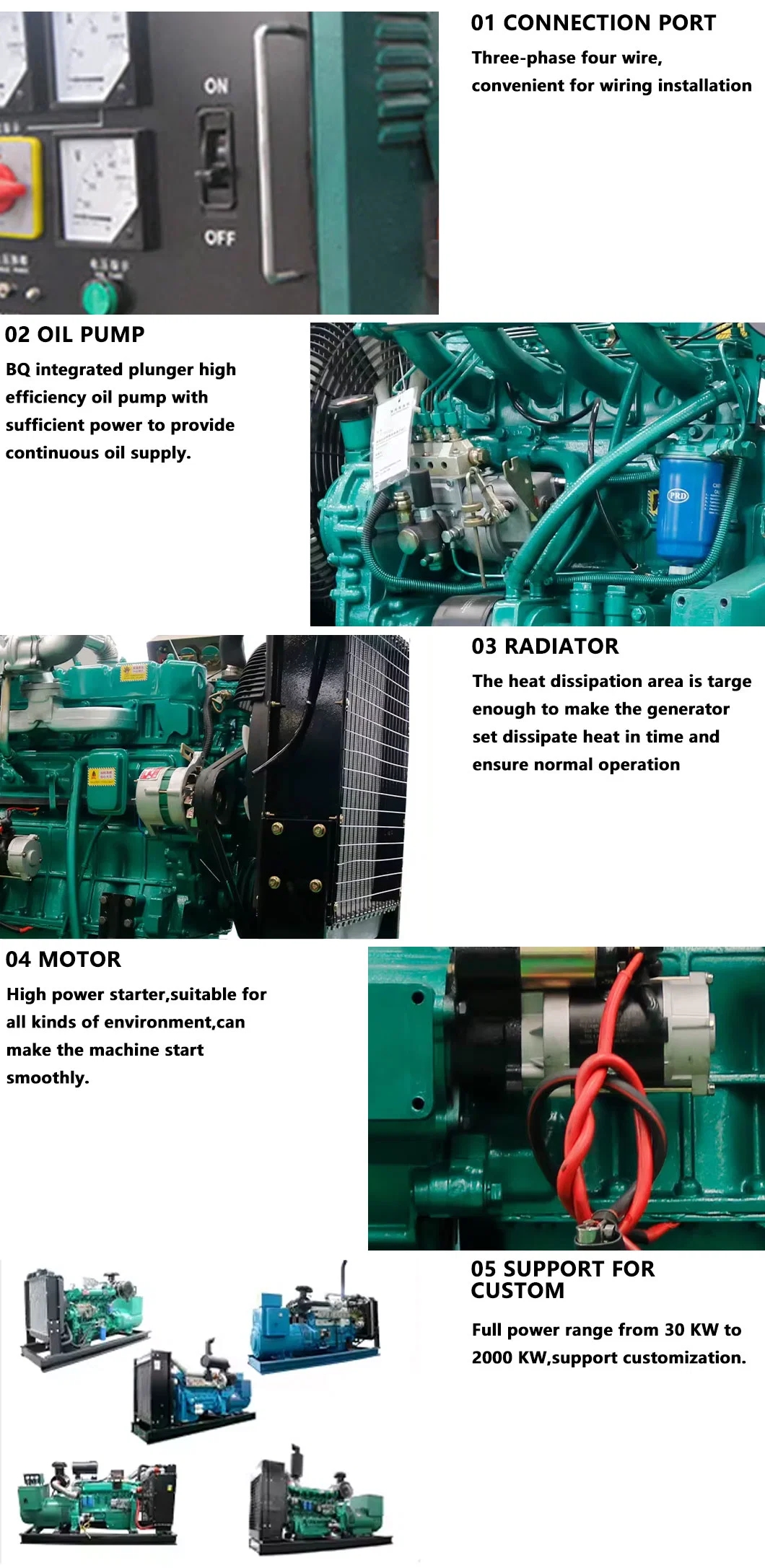
Applications of Diesel Generators in Industrial Settings
Diesel generators find extensive use in a variety of industrial applications where reliable backup power is crucial for uninterrupted operations. Some common industrial applications of diesel generators include:
1. Manufacturing Plants: Manufacturing plants rely on a steady and uninterrupted power supply to operate heavy machinery, production lines, and other critical equipment. Diesel generators serve as backup power sources to prevent costly downtime and production losses during power outages.
2. Data Centers: Data centers house critical IT infrastructure that requires continuous power to ensure data integrity and accessibility. Diesel generators are used to provide backup power in the event of grid power failures, protecting data center operations from disruptions.
3. 500kw diesel generator for construction tools : Hospitals and healthcare facilities require reliable power to support life-saving medical equipment, lighting, and climate control systems. Diesel generators are essential for providing emergency backup power during blackouts or natural disasters to ensure continuity of care.
4. Telecommunications: Telecommunication networks rely on uninterrupted power to maintain connectivity and communication services. Diesel generators are deployed at cell towers, data centers, and network hubs to provide backup power in case of grid outages or emergencies.
5. Construction Sites: Construction sites often operate in remote locations or areas with unreliable power infrastructure. Diesel generators are used to power construction equipment, lighting, and temporary facilities, enabling construction projects to proceed smoothly without dependence on the grid.
Benefits of Diesel Generators for Industrial Applications
Diesel generators offer several key advantages that make them the preferred choice for industrial applications:
1. Reliability: Diesel generators are known for their robustness and reliability, making them ideal for providing backup power in critical industrial operations. Diesel engines are durable and can withstand heavy loads and harsh operating conditions, ensuring consistent performance when needed most.
2. Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient compared to gasoline engines, providing higher energy output per unit of fuel. This translates to lower fuel consumption and operating costs over the lifetime of the generator, making diesel generators a cost-effective choice for industrial applications.
3. Quick Start-up: Diesel generators have quick start-up times, allowing them to provide power within seconds of a grid power failure. This rapid response time is crucial for industrial operations that require immediate backup power to prevent disruptions and losses.
4. Longevity: Diesel generators have a longer lifespan compared to other types of generators, thanks to the durability and efficiency of diesel engines. With proper maintenance and servicing, diesel generators can operate reliably for decades, offering a dependable power source for industrial facilities.
5. Versatility: Diesel generators are versatile and can be used in a wide range of industrial applications, from small-scale operations to large manufacturing plants. They can be easily integrated into existing power systems and can be customized to meet specific power requirements, making them a flexible solution for diverse industrial needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diesel generators play a vital role in powering industrial operations around the world, providing reliable backup power when grid power fails. With their durability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, diesel generators have become indispensable assets in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, telecommunications, and construction. As technology continues to evolve, diesel generators are expected to further improve in terms of performance, efficiency, and environmental sustainability, ensuring their continued relevance in the industrial landscape.
